Window Sliding Technique
This technique involves taking a subset of elements from an given array and slide this subset or expand it or shrink to satisfy some condition
Problem-1 Given an Array of int and a number k, find the maximum sum of k consecutive elements. example: int arr[] = {1,40,30,10,20,5}; int k = 3; output 80
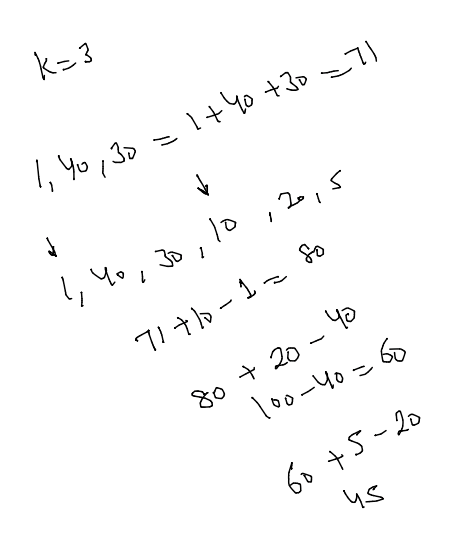
Brute force Approach is
class WindowSlidingTechnique {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 1, 40, 30, 10, 20, 5 };
int k = 3;
int maxSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i + k - 1 < arr.length; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
sum += arr[i + j];
}
if (sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
}
}
System.out.println("Max Sum " + maxSum);
}
}TC is O(n-k)*k and SC O(1)
😎 Now we focus on optimise solution , using window sliding technique. The Approach is first keep the total of k elements and when we traverse / move then add the next element (e.g arr[i] array of ith element) and subtract the starting element (e.g arr[i-k] array of i-k th element). See the following image.
static void windowSlide() {
int arr[] = { 1, 40, 30, 10, 20, 5 };
int k = 3;
int slideSum = 0;
int maxSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
slideSum = slideSum + arr[i];
}
maxSum = slideSum;
for (int i = k; i < arr.length; i++) {
slideSum = slideSum + arr[i] - arr[i - k];
if (slideSum > maxSum) {
maxSum = slideSum;
}
}
System.out.println("Max Sum " + maxSum);
}TC is O(N) and SC O(1)
Problem-2 Given an unsorted array of positive integers. Find the subarray which is sum is equal to given sum.
e.g int arr [] = {10,20,30,40,50}; int sum = 90
The Brute Force Approach is
public class SubArrayGivenSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 290 };
int sum = 90;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int total = 0;
for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {
total += arr[i];
if (total == sum) {
System.out.println("Sum found...");
return;
}
}
}
System.out.println("No Such Sum....");
}
}
The Optimise Approach is Using the Window Sliding Technique. Keep adding the element in the window till window<sum else minus the element from the window , if window>sum.
static void windowSlideApproach() {
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 290 };
int sum = 370;
int startIndex = 0;
int slideSum = arr[0]; // put the first element in slide sum
// start from the first element
for (int i = 1; i <= arr.length; i++) {
while (slideSum > sum && startIndex < i - 1) {
slideSum = slideSum - arr[startIndex];
startIndex++;
}
if (slideSum == sum) {
System.out.println("Sum found...");
return;
}
// checking not going out of bound becuase loop is till i<=arr.length to take care the last element sum comparsion
if (i < arr.length) {
slideSum = slideSum + arr[i];
}
}
if (slideSum == sum) {
System.out.println("Sum found...");
return;
}
System.out.println("No Such Sum");
}
Problem-3 NBonacii Series, Given is 2 integers n = 3 and nthTerm is 15 , So Fibonacci When is n is 2 and if n is 3 it is become Tribonacci and n is N so it is called NBonacci.
e.g For example, a 3-bonacci sequence is the following:
0 0 1 1 2 4 7 13 24 44 81 149 274 504
class NBonacciNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sliding = 3;
int nthTerm = 15;
int arr[] = new int[nthTerm];
// in sliding three the 1th and 2st term is 0 and 3rd term is 1
for (int i = 0; i < sliding - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
arr[sliding - 1] = 1;
int start = -1;
int second = 0;
for (int i = sliding; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
if (start != -1) {
second = arr[i - 1] - arr[start];
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] + second;
} else {
arr[i] = arr[i - 1];
}
start++;
}
for (int ele : arr) {
System.out.print(ele + " ");
}
}
}Problem-4 Count the distinct elements in every window of size k.
Hint: Window Sliding with Hashing
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CountDistinctElementInWindow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 7 };
int sliding = 4;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i + sliding - 1 < arr.length; i++) {
countMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int j = i;
int k = 0;
while (k < sliding) {
if (countMap.get(arr[j]) == null) {
countMap.put(arr[j], 1);
} else {
int f = countMap.get(arr[j]) + 1;
countMap.put(arr[j], f);
}
j++;
k++;
}
int count = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> e : countMap.entrySet()) {
if (e.getValue() == 1) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
Prefix Sum Technique or PreComputation Technique
Given an Array and we want to do the sum of given range and range queries will be perform N Number of times
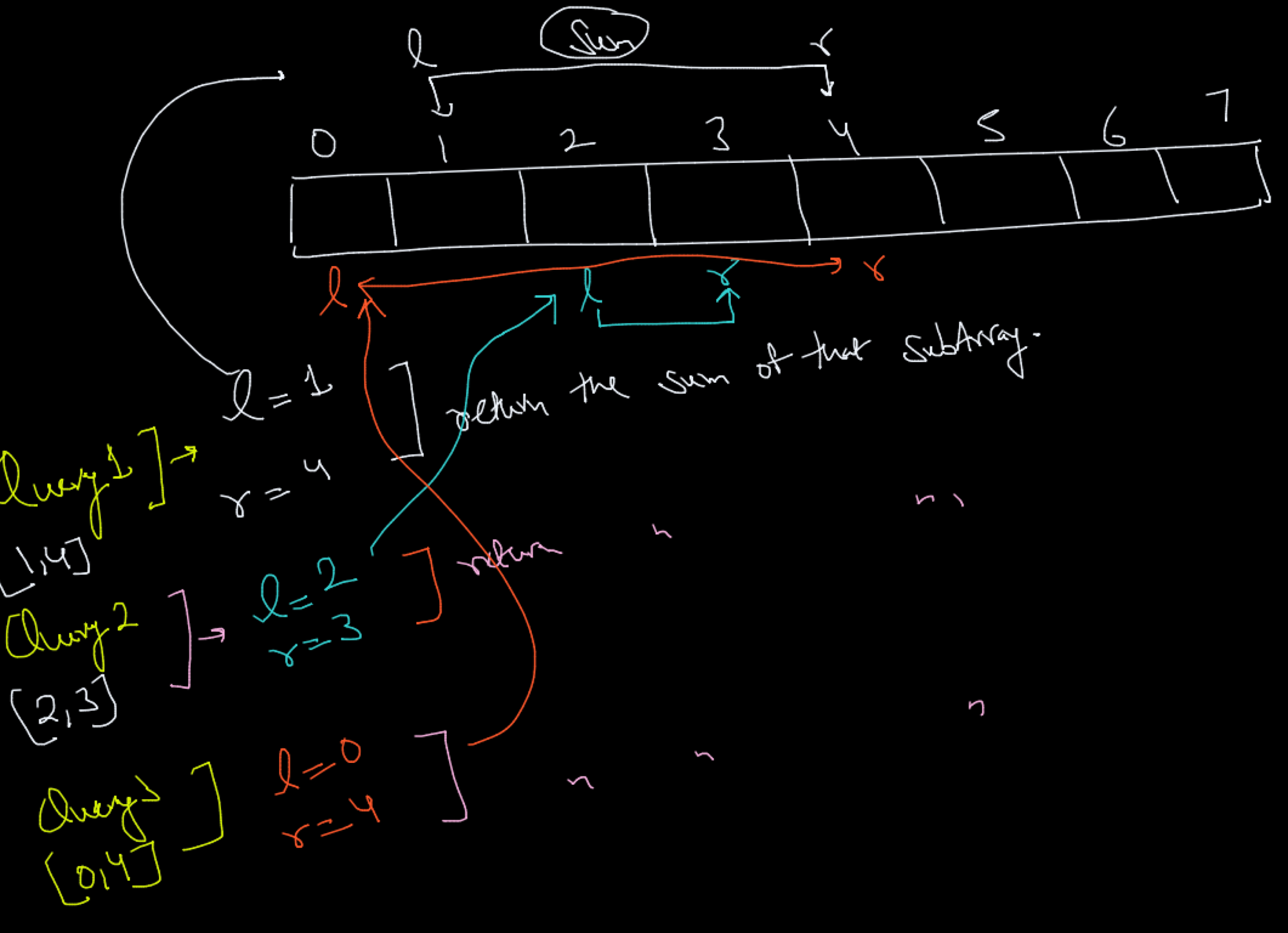
The Brute force way is Loop for Queries and then loop for sum and it solve in N^2 TC. Assume if the N is 10^6 and Q is 10^6 so it will do lot of computation.
So to solve these problems we need some preprocessing technique.
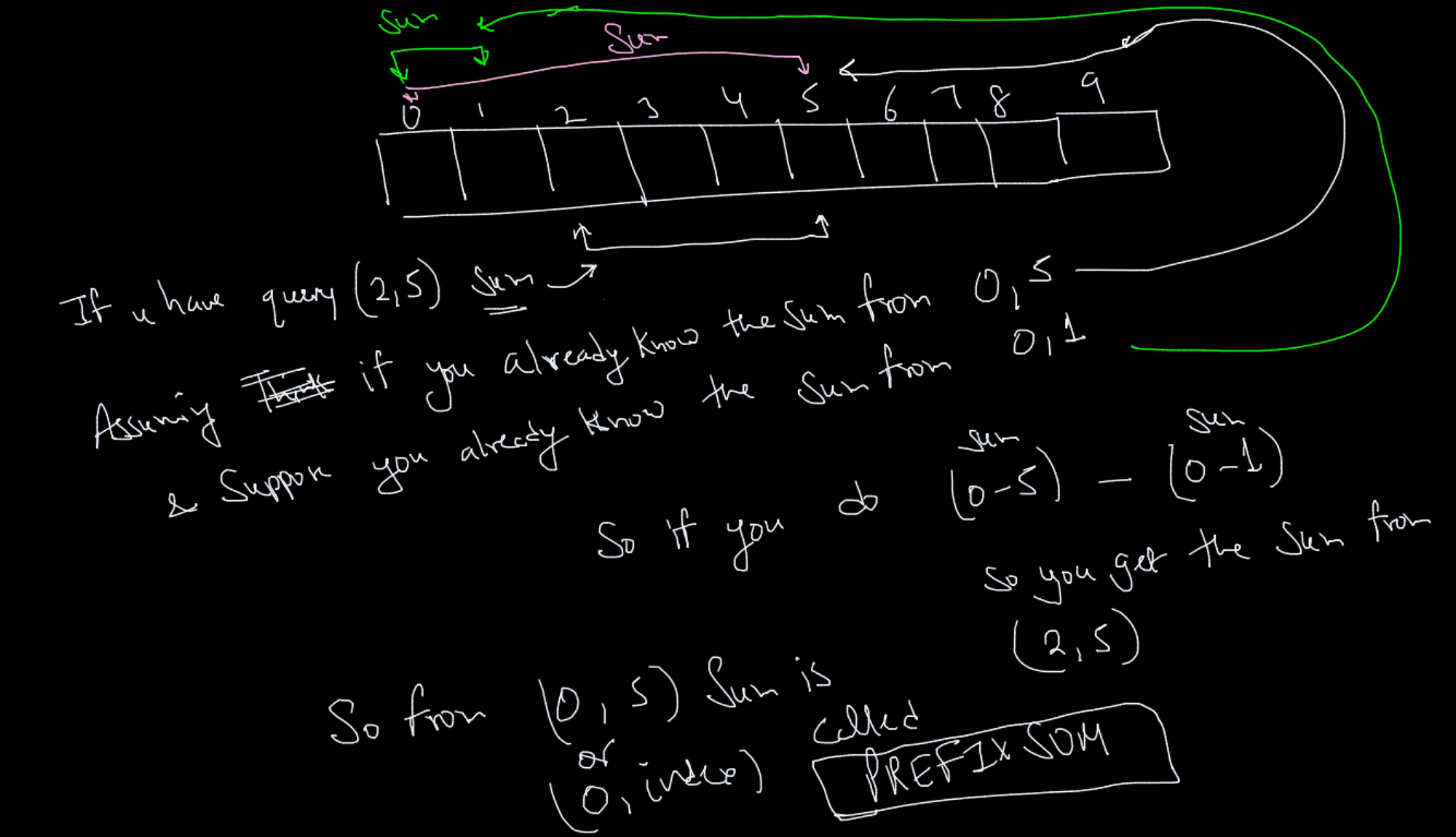
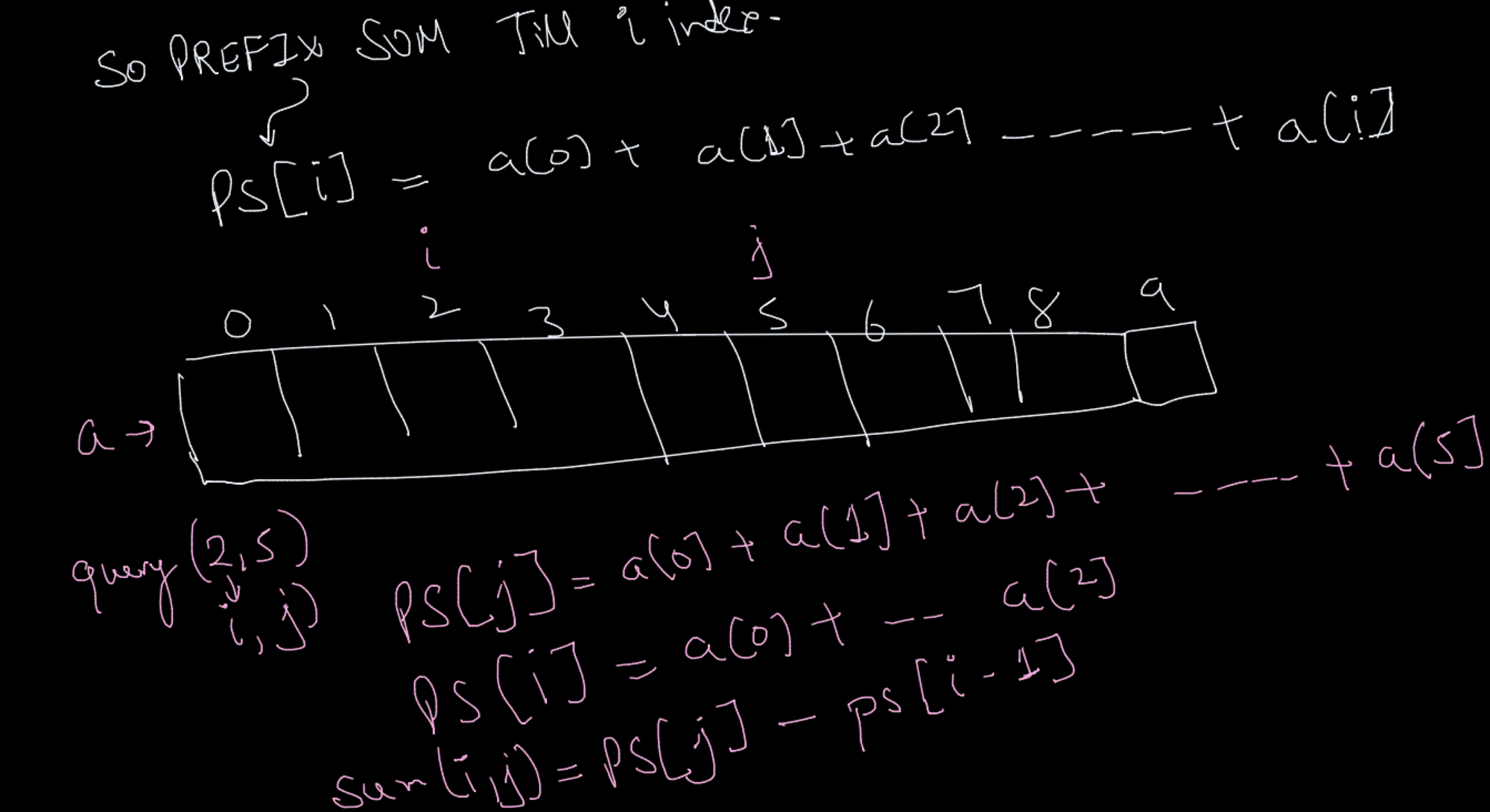

Algorithm is
for(int i =1 i<n; i++){ // it start with i = 1 because you do prefix sum arr[i-1] otherwise you get ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException exception
arr[i]+= arr[i-1]; }
Note: Either you will create prefix array/ or temper the original array.
Now After this takes Queries One by One
O(Q) for Q Queries
int result = arr[r] - arr[l-1] ; // TC O(1) // r for right and l for left
if l is Zero so you need to return the sum till arr[r]
if(l==0){
return arr[r];
}
public class PrefixSum {
static int getRangeSum(int prefix[], int l, int r) {
if (l == 0) {
return prefix[r];
} else {
return prefix[r] - prefix[l];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 2, 5, 10, 1, 3, 4, 5 };
int prefixSum[] = new int[arr.length];
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < prefixSum.length; i++) {
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i];
}
for (int i : prefixSum) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(getRangeSum(prefixSum, 0, prefixSum.length - 1));
System.out.println(getRangeSum(prefixSum, 2, 5));
}
}
Problem-1 Find the Equilibrium point in given integer array.
example: {8,4,4} No , example: {4,-2,2} Yes
static void bruteForce() {
int arr[] = { 4, 2, -2 };
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// do left sum
int leftSum = 0;
int rightSum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
leftSum += arr[i];
}
// do right sum
for (int k = i + 1; k < arr.length; k++) {
rightSum += arr[k];
}
if (leftSum == rightSum) {
System.out.println("Yes");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("NO");
}The optimise approach is we do the prefix sum and then compare the left side sum with the right side sum.
static void prefixApproach() {
int arr[] = { 4, 2, -2 };
// first calculate the total sum of an array
int sum = 0;
for (int ele : arr) {
sum += ele;
}
// now traverse array from left to right and compare the sum value
int leftSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (leftSum == sum - arr[i]) {
System.out.println("Yes");
return;
}
leftSum += arr[i];
sum -= arr[i];
}
System.out.println("No");
}Two Pointer Technique
Used for searching pairs in a sorted array.
Example is Pair Sum we already did in Tutorial -3
Try yourself , Find the Average Pair b/w 2 numbers in given array.
That's all Folks , Meet you in next Tutorial 😀
